Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a software program that does repetitive tasks based on rule-based algorithms. RPA can be regarded as a subset of the bigger technology that Artificial intelligence (AI) is.
AI is the collective term used for all cognitive computing technologies including RPA, machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. In short, Artificial Intelligence is a program that can sense, reason, act, and adapt according to changing data scenarios.
AI is the underlying technology that empowers RPA. RPA is attended automation, whereas AI is unattended automation. Together, they make it possible to automate repetitive tasks that do not require human attention and cognitive tasks that require human attention.
READ : Here’s how AI Chatbots can Lead to Customer Retention
How do these two technologies differ from each other?
AI uses unstructured inputs and develops its own logic to perform operations. RPA requires structured inputs and pre-defined rules to operate. This is the single aspect that distinguishes both the technologies from each other.
However, there are several other aspects that differentiate RPA and AI as well. They are summarized in the table below:
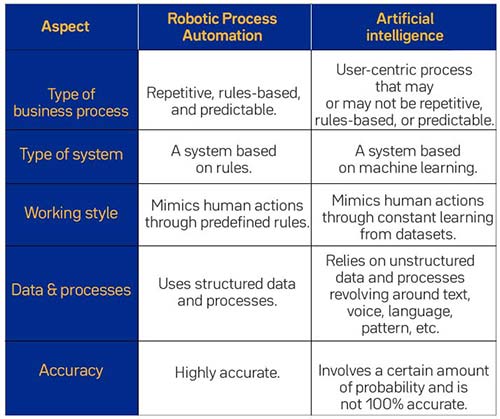
Of course, both technologies can deliver value as standalone applications. However, the maximum value from these technologies can be derived only when they are used together. In fact, AI & RPA complement each other perfectly.
AI & RPA: Superhero and the sidekick
When AI & RPA work together, they create end-to-end automation. RPA takes care of process-driven operations that can be automated based on rules. The rules are the processes that a human would otherwise follow to carry out the process. Through automation, RPA helps in processing a large volume of transactions that a human will not be able to handle.
AI can fill in where RPA falls short. For example, RPA handles rule-based tasks with precision. Anything beyond the scope of the defined rules cannot be handled by RPA. AI, with its machine learning and deep learning capabilities, can handle such out-of-scope tasks of RPA and aid in end-to-end automation. The combined use of Artificial intelligence and Robotic Process Automation is referred to as intelligent Automation.
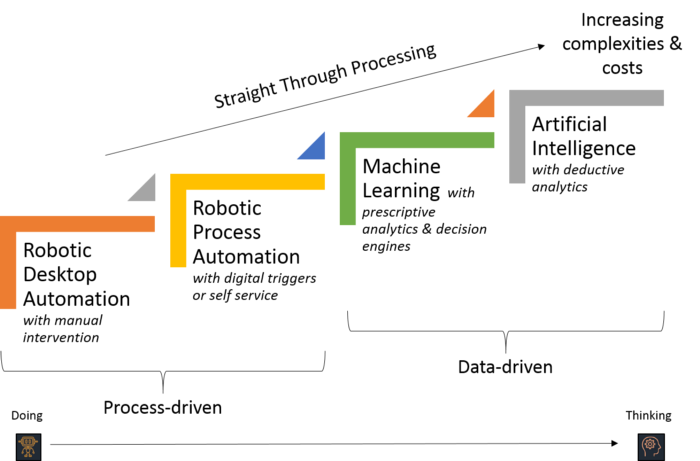
Intelligent automation
When used together, AI and RPA result in what is known as ‘intelligent automation’. Intelligent automation facilitates end-to-end business process automation and also paves the way for organizational digital transformation.
SEE : Intelligent Process Automation: The next wave of RPA
From heavy-duty manufacturing to sensitive healthcare, Intelligent automation has already started to create a stir across all industries. It is the best fit for industries and business operations where there is a huge volume of process-driven and data-driven tasks. What makes intelligent automation powerful is that it can automate tasks at all stages — right from customer-facing applications to backend behind-the-scenes tasks.
Benefits of Intelligent Automation
AI and RPA together are enabling businesses to function at a new level of productivity. They are adding IT muscle power to organizations and empowering them to deliver high-quality work with continually decreasing costs.
Here are some of the direct benefits that the two technologies are bringing to businesses:
- Augmented business productivity
Intelligent automation handles a large volume of low-key tasks that are transactional and repetitive in nature. They channel the time and resources of the workforce for high priority tasks that deserve their personal time and attention.
As employees have more time at their hands, they will be able to devise better strategies or fine-tune existing ones that can lead the business forward. RPA ensures that all the routine work is taken care of without any lapses. All tasks that fall beyond the rules of the RPA system can be handled by the AI system. Human intervention will be required only in instances when the systems need direction to move forward. - Automation of high-volume recurring tasks
Low-volume recurring tasks refer to those tasks that do not necessarily demand the time and attention of the employee. For example cross-checking two documents side by side, entering data into the system from physical or digital records, and so on.
These tasks can be easily automated using a rule-based algorithm. The algorithm can work based on triggers set within the system or can be triggered by the employee using a command action. Since the tasks are recurring in nature and are in high volume, it is possible to achieve scalability in operations.
- Reduction of manual errors
Any recurring task which occurs in large numbers is repetitive, and is handled by human personnel is prone to errors. Despite the high level of expertise and working experience of the personnel, everyday factors like health, working environs, etc. can have an impact on the quality of work. Also, there could be exhaustion caused due to long hours of working.
These factors can invariably cause errors to creep into the system. Intelligent automation can effectively eliminate these errors. RPA, which always works based on predefined rules does not make errors. AI, on the other hand, can learn from the transactions and can tweak its working to avoid mistakes. As a result, there will be a serious reduction in manual errors.
- Improves data management
RPA requires structured data, to begin with. This creates a mandate that the organization create a uniform system of data management and organization. As with any other process, proper organization of records and data amplifies productivity.
Also, it makes it easy to create datasets that can be used to train AI models. In a way, it can be rightly said that intelligent automation enforces a change from the grassroots level that results in better results.
- Maximizes process transparency
Intelligent automation works on straight-forward rules that are not compromised at any level. There is no personal bias, undue influence, or any other personal factor that hampers its productivity. It gives complete transparency into how the process works and how results are achieved. This transparency creates a level field within the organization where stakeholders from various backgrounds could be collaborating on a single project.
The transparency in operations also works in the favor of the organization when it is subject to data protection and regulation rules set out by local laws and regulations.
Industries where intelligent automation is becoming active
According to McKinsey’s The social economy report, 61% of an employee’s average workweek is spent on everyday tasks. These are tasks that do not necessarily demand the physical and cognitive resources of the employee. They can be easily automated with the help of intelligent automation. The scope for such automation is not restricted to IT alone. Every other industry where recurring tasks are commonplace can make use of it. For instance:
READ : Why do Companies choose Intelligent Automation?
- Financial services
The centuries-old banking and financial services industry is up for an overhaul. Perhaps, the BFSI industry is the one that is ripe enough for the disruption caused by intelligent automation. With millions of customers and billions worth of transactions, it generates massive amounts of data that intelligent automation can leverage.

With intelligent automation, financial services can automate key services that customers use on a daily basis. From reducing manual intervention in processing trade documents to automating retail customer payment operations, the possibilities are nearly endless for automation in financial services.
- Insurance
One of the biggest challenges for insurance companies around the world is tackling the sheer volume of claims involved. Intelligent automation can be of great support here by eliminating the need for employees to manually peruse each policy to determine claim-worthiness.
By automating the claim processing tasks, or at least the repetitive portion of it with RPA, insurance companies can save a lot of time, effort, and other resources. It also reduces the number of errors that would otherwise creep in and result in compliance breaches.
Some other use cases for intelligent automation in insurance include name screening, customer research, pattern detection in claims, validation of customer data against KYC norms, etc.
- Retail
In the retail space, especially in e-retail, intelligent automation has endless scope. From enabling robot-assisted warehouse picking to optimizing the supply chain routes for quicker deliveries, intelligent automation can be a friendly assistant to retailers in several ways.
Intelligent automation reduces cost, accelerates work, and also helps retailers devise new ways to serve better customer experience to their customers.
- Automotive
Mary Barra, CEO, General Motors, is of the opinion that the automobile industry is changing more today than it has in five whole decades. The change is not restricted to introducing a new model of car or an advanced engine system. They run deeper and broader and are gearing up to transform the automotive industry from the grassroots level.
Intelligent automation can penetrate every stage of automotive manufacturing and create new efficiencies that were not possible earlier. To begin with, there will be rapid automation of tasks and processes in the assembly line that will fast-track manufacturing, reduce manual errors, and even accidents. Furthermore, it will now be possible to estimate the need for raw materials, production time, etc. with accuracy like never before. All decisions, be it related to planning or introducing a new offer in the market, can be data-driven.
- Manufacturing
We are entering the age of Manufacturing 4.0. Intelligent automation is going to kickstart the next revolution in manufacturing in less than a decade.
How exactly is intelligent automation influencing manufacturing? Manufacturing is getting swarmed with coin-sized IoT devices that can attach themselves to any surfaces — right from simmering hot boilers to robotic arms that are in constant swing actions. These devices can emit data to a centralized server where the data can be further dissected with analytical tools. Data-driven manufacturing activities will eventually lead to efficiencies.
Intelligent automation: Ushering the age of the machines
RPA and AI have picked up global interest in the last 12 months.When RPA and AI work in conjunction, they create new efficiencies that have not been experienced before. Together, they make intelligent automation happen. Intelligent automation is reckoning a future where man and machine will work together to augment productivity, reduce inefficiencies, and deliver superior customer experience.
Would this have been possible in the past? Not necessary. It is only with the explosion of data creation, internet bandwidth availability, and the sharp fall in IT hardware prices that these technologies have finally become affordable for all. From just-launched startups to corporations that have been around for a while, automation is now within the reach of all.

